1. General context of smart lighting system in commercial buildings
Following the development of the country's industrialization and modernization, urban areas with high-rise commercial buildings develop rapidly. According to statistics, Vietnam ranks 22nd with 29 buildings over 150m high, 20th with 7 buildings over 200m high and 9th with 2 buildings over 300m high. The potential for energy saving in construction works is estimated at 30-35%, the annual rate of increase in used floor area is over 40%.
Currently, Vincom Landmark 81 building with 461.3 m high is the tallest building in Vietnam [1]. Smart lighting for commercial buildings falls within the general context of smart buildings and smart cities.
Most smart buildings use BMS (Building Management System) building management system, including:
- Power, water and gas supply system;
- Lighting systems;
- Elevator system;
- Safety protection system, fire protection;
- Communication system etc.
With the rapid development of LED lighting technology, 5G generation Internet, IoT technology, big data technology and artificial intelligence, it is possible to realize smart lighting for commercial buildings.
2. LED lighting technology gives building lighting a whole new quality
Lighting for commercial buildings includes:
- General lighting for staterooms, halls, community rooms, corridors, supermarkets etc.
- Lighting for apartments;
- Lighting for landscape outside the building;
- Lighting for garden, swimming pool, internal road.
Lighting technology passed through 3 periods with different requirements [2]:
- The first period should pay attention to ensure visual comfort;
- The second period ensured visual comfort while using energy economically and efficiently;
- Currently, lighting technology has moved to a new era, in addition to satisfying the requirements of visual comfort and energy saving, it also meets emotional requirements. The light not only affects the visual system, but also brings happiness and sadness, creates conditions for people's mental and physical health. Emotional lighting or green lighting or ecological lighting thoroughly imitate sunlight and use a new generation of LED lights. The LED Sunlight has true colors like daylight and can flexibly control the intensity, color and CRI color rendition of light according to human emotions.
All requirements for the new lighting system are a combination of two factors:
- New generation LED: LED Sunlight;
- Intelligent control system.
We will specifically consider the implementation of smart lighting systems for buildings as follows:
3. Basic elements of Smart lighting system
A Smart lighting system consists of 3 main parts with the block diagram (shown in Figure 1).
3.1 Light(s)/Lamp(s);
3.2 Sensors: sensing parameters of light space and human activity;
3.3 Controller.
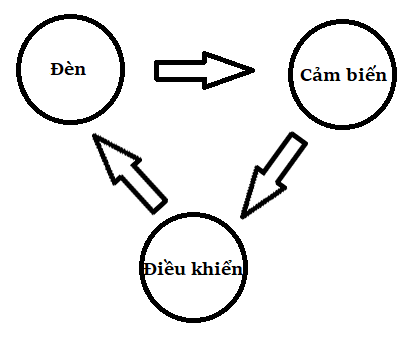
Figure 1. Main elements of smart lighting system
3.1 Lighting lamps are LED Sunlights with high luminous flux-to-power (lumen/W) ratio, at least 100 lm/W and very high color rendering coefficient CRI >90. They are suitable for different purposes in terms of aesthetic appearance.
Compared with lighting with gas discharge lamps such as fluorescent lamps, compact lamps, LED lamps have good light quality, allowing to adjust (dimming) from 0-100% of luminous flux and saving 50% of power consumption. Their life is increased 4 times, in addition the LED has high mechanical strength and it is hard to break, does not contain mercury, does not emit UV rays. The only barrier that the LED encounters is the cost of 3-4 times higher than gas lamps, but over time LED prices have fallen sharply.
3.2 The Sensors used in smart lighting system can be classified into two categories:
a) The presence sensor (proximity sensor) recognizes the object entering the sensing area to turn the light on and off.
b) Optical sensor (photo sensor) senses outdoor natural light levels to turn lights on and off according to natural light levels.
In the type of presence sensor, two technologies are commonly used:
- Passive InfraRed sensor (PIR): Figure 2 presents a schematic diagram of a PIR sensor that senses infrared thermal energy emitted by the human body. They are sensitive to moving objects and sense infrared rays with a wavelength of 10 mm. The infrared sensor is made from a material with a pyrothermal effect that converts infrared heat into an electrical signal.
.jpg)
Figure 2. Infrared Presence Sensor
The output signal is amplified, compared and applied to the circuit to turn on and off the light, open the door automatically or gives an alarm when there is a theft.
The detection area of the infrared sensor is an enlarged cone. Most infrared sensors can sense the movement of the human arm at a distance of 4-5m, the whole body at 12m. Sensors are usually located at a height of 2-3 m.
- Cảm biến siêu âm (Ultrasonic sensor)
.jpg)
Figure 3. Working principle of ultrasonic sensor
Figure 3 is the schematic diagram of the ultrasonic sensor. Ultrasound is a mechanical wave with a speed greater than the speed of sound (300 m/s) that the human ear cannot perceive. The ultrasonic sensor consists of an ultrasonic emitter (made of ceramic material) that emits an ultrasonic beam into space. When encountering an object, the ultrasonic beam is reflected and received by the receiver. According to the Doppler effect, the frequency of the reflected wave will change if the object moves, so the presence of the object can be detected in the coverage area. To avoid confusion with other frequencies such as hearing aids, TV remotes, etc. Ultrasonic sensors operate at frequencies above 32kHz, providing continuous coverage (no gaps) and are more sensitive than infrared sensors. For example, a hand movement can be detected at 7.5m, arm at 9m, whole body at 12m. However, the presence signal (ON) can be wrong due to air flow, door moving etc. Most ultrasonic sensors work well in ceiling spaces lower than 4.2 m, however there are some number of detectors moving at a height of up to 9m.
- Photo sensor is a photodiode, phototransistor semiconductor device, with a very large dark resistance compared to the light resistance, which changes state according to the luminous flux of the light.
Next is the means to control the actuating mechanism to turn on or off the light(s) (Figure 4).


Figure 4. Photo sensor
The features and installation locations of the sensors are given in the following table:
|
Installed position |
Technology |
Cover angle (degree) |
Cover area (m2) |
Optimal height (m) |
|
Ceiling Ceiling Ceiling Wall Wide corner Wall Narrow corner Corridor Above High corner High ceiling |
Ultrasonic Infrared Ultrasonic + Infrared Ultrasonic Ultrasonic + Infrared Infrared Infrared Ultrasonic Infrared Combination Combination |
360 360 360 180 110-120 170-180 12 360 12-120 110-120 360 |
25-2745-180 27-90 27-90 25-27 12 27-90 50 30 30 150-300 150-300 |
2,4-3,6 2,4-9 2,4-3,6 1,2-1,4 2,4-4,5 1,2-1,4 2,4-4,5 2,4-4,5 9 2,4-3,6 2,4-3,6 |
3.3 The controller receives signals from the sensors to act on, off, dimming, changing the color of the lights according to a programme on the microcontroller. Connection technologies are divided into two main categories: wired connection and wireless connection.
Wired connection includes the following technologies: DALI (Digital Addressable Lighting Interface); Ethernet; BACnet (Building Automation and Control networks); Lonworks.
Wireless connection includes the following technologies: Zigbee; WIFI; Bluetooth, Jennet-IP Wireless Network; Enocean Wireless Technology etc.
With the development of mobile network technology, internet and cloud computing, the trend of smart lighting systems which is monitored and controlled remotely via mobile devices has been increasingly being developed.
Figure 5 presents the network structure of the smart indoor lighting system. The lights are connected wirely or wirelessly to a gateway or data collector. Gateways and mobile devices from multiple locations are connected to the interner receiver. Control devices, usually smartphones or computers, are connected to the gateway through the Router, so that the lights are controlled via the internet according to pre-installed scenarios.
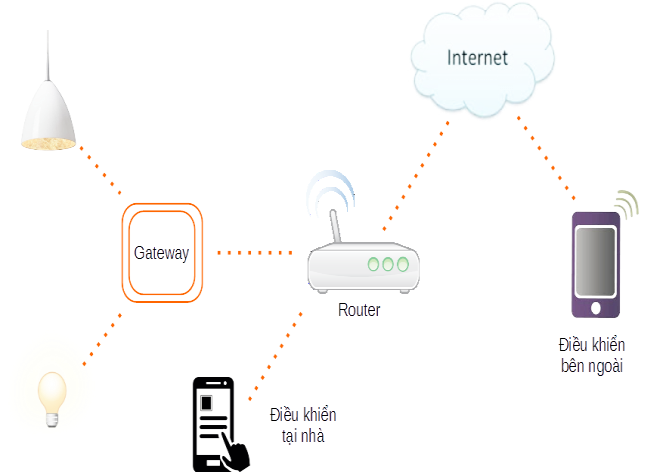
Figure 5. Lighting control by smart phone
.png)
Figure 6. Smart control of the meeting room
Figure 6 describes a design integrated hardware and software of a controller set up on a smartphone which uses wireless technology for the purpose of lighting for halls, showrooms, home control panels with many lighting scenarios according to customer requirements [3].
4. Optical fiber decorative lighting
Optical Fiber Lighting [4] is also known as non-electrical lighting. The structure of an optical fiber lighting system consists of 3 parts (Figure 7):
- The source is the LEDs and the condenser controller changing the color of the light;
- Optical fibers are fibers of silica material that allow light transmission over long distances with very little loss;
- Accessories include specially shaped optical receivers.
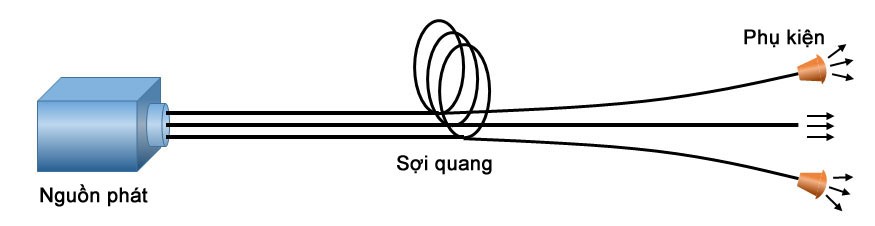
Figure 7. Optical fiber landscape lighting
Fiber optical lighting systems are often used for landscape lighting to create aesthetics for commercial buildings, supermarkets, garden miniatures, swimming pools. The advantages of this system are:
- Create vivid images and colors according to many scenarios;
- Completely insulated, therefore very safe, durable, allowing to be applied outdoors or underwater;
- Consumes very little energy.
Figure 8 shows some optical fiber illumination images.
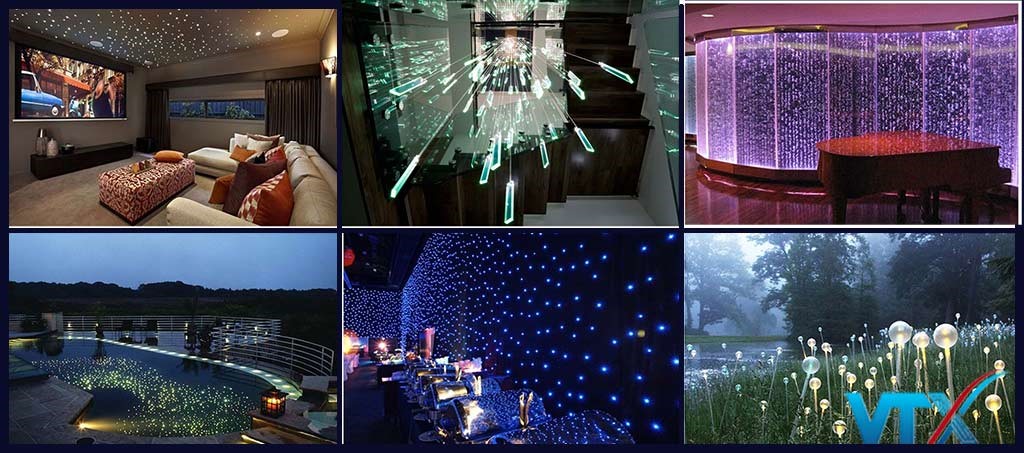

Figure 8. Decorative lighting with optical fiber
5. Conclusion
Lighting by LED technology combined with modern control system, internet Wi-Fi, IoT technology, Big data technology and AI (artificial intelligence) allows to create smart lighting system for buildings and commercial houses, ensure the quality of light according to emotions and use energy economically and efficiently. Vietnamese technicians and managers need to master this technology to help Vietnam catch up with modern lighting trends of countries in the region and the world./.
Assoc. Prof. Dr. Le Van Doanh
& Vietnam Energy Conservation and Energy Efficiency Association
References
[1] Skyscrapercenter statistics up to 2019.
[2] Economical and efficient lighting techniques - Science and Technology Publishing House, 2000, Editor-in-Chieft Le Van Doanh.
[3] Report of Rang Dong R&D Center - HNKH 2020.
[4] https://www.optical landscape lighting.


